Patterns of Venetoclax Sensitivity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
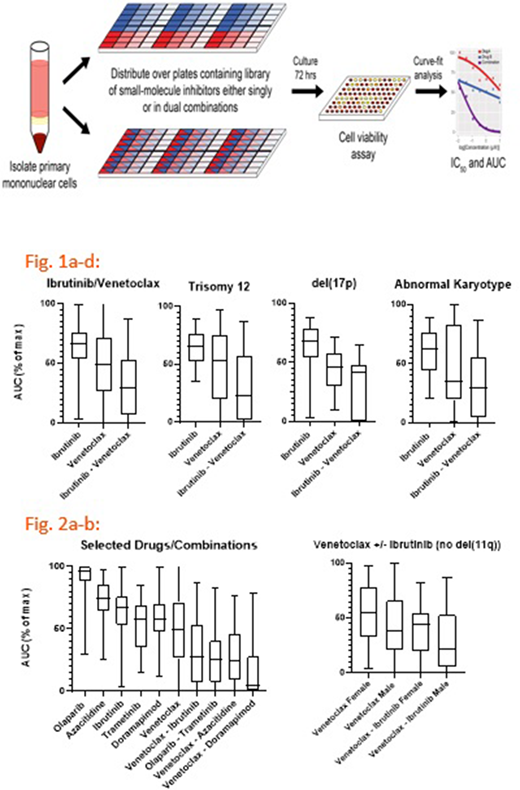
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is predominantly a disease of older adults. The 5-year overall survival is 70-91%, depending on Rai/Binet stage at diagnosis (80% overall), and although a subset of CLL takes a very indolent course, it can be aggressive as well. Disease course and responsiveness to therapeutic agents may be predictable, to some degree, based on specific genetic lesions or other patient population characteristics. Monotherapies targeting specific cell pathways are rapidly increasing in prevalence. Ibrutinib (Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor) has shown promise as a single agent as well as in combination with other agents. In particular, ibrutinib has shown efficacy in combination with venetoclax (inhibitor of cell death suppressor BCL2). This combination appears to be particularly potent in patients with a del(11q) karyotype. Cytogenetic information is used already in several other leukemias to inform prognosis and treatment. Although CLL is a disease of monoclonal proliferation, precise definition of the diseased clone will allow for more individualized treatment. Stratification of drug sensitivity based on genetic and cytogenetic features will directly affect patient outcomes in CLL.
Primary patient mononuclear cells (from either peripheral blood or bone marrow) were plated ex vivo with a panel of 49 drug combinations and the 16 respective single agents (SA) in 384-well plates using 10,000 cells/well. Drugs were tested in 7-point concentration series; wells with drug combinations were added at fixed molar ratios. Cell viability was assessed after a 72 hour culture period. In this assay, primary cells maintain viability but do not proliferate. In CLL, the most frequent mutations were: del(17p); del(11q); del(13q14); trisomy 12; complex karyotype (at least three chromosomal aberrations).
Selected analysis of these data from 157 unique patients were performed by isolating the most potent inhibitors (defined by lowest median AUC) either as a single agent or in combination with known treatments. These were evaluated with nonparametric tests (Kruskal-Wallace, Mann-Whitney, Spearman rank coefficient) on the statistical software Prism. By subdividing the data by available genetic and cytogenetic information, patterns that have not been previously described in the literature emerged.
In the cohort of patients with any karyotypic abnormality (not complex karyotype), SA venetoclax and the combination of venetoclax-ibrutinib (VEN/IBRUT) were equivalently effective with no significant difference in efficacy observed between SA venetoclax and the combination. As previously described, del(11q) independently predicts increased efficacy of SA venetoclax and VEN/IBRUT, and this efficacy was validated by ex vivo potency here as well. However, we show that male gender is an independent predictor of potency in both SA venetoclax and VEN/IBRUT as well.
Interestingly, doramapimod (an inhibitor of p38 MAP kinase) was not particularly potent as a SA, however, the combination of venetoclax-doramapimod (VEN/DORA) proved to be the most potent of all combinations tested, more potent than even VEN/IBRUT. This effect could not be replicated in any subgroup, as VEN/DORA samples for the entire cohort were relatively limited (n=31).
Although this analysis has inherent limitations, including underpowered data to analyze in less frequent cytogenetic events (e.g. del(6q)), we did find significant patterns of potency. These may or may not translate to clinical efficacy in CLL and do not address any potential toxicity. However, these data suggest future directions for more targeted research on these drugs and drug combinations.
Tyner:Petra:Research Funding;Janssen:Research Funding;Seattle Genetics:Research Funding;Incyte:Research Funding;Genentech:Research Funding;Constellation:Research Funding;AstraZeneca:Research Funding;Aptose:Research Funding;Gilead:Research Funding;Takeda:Research Funding;Syros:Research Funding;Agios:Research Funding;Array:Research Funding.Druker:EnLiven:Consultancy, Research Funding;Gilead Sciences:Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Cepheid:Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Dana-Farber Cancer Institute:Patents & Royalties;Bristol-Myers Squibb:Research Funding;Blueprint Medicines:Consultancy, Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Aptose Therapeutics Inc. (formerly Lorus):Consultancy, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;ARIAD:Research Funding;Third Coast Therapeutics:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;The RUNX1 Research Program:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Pfizer:Research Funding;Patient True Talks:Consultancy;Oregon Health & Science University:Patents & Royalties;Novartis Pharmaceuticals:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding;MolecularMD (acquired by ICON):Consultancy, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Millipore (formerly Upstate Biotechnology):Patents & Royalties;VB Therapeutics:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Vivid Biosciences:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;ALLCRON:Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Amgen:Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Aileron Therapeutics:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Merck & Co:Patents & Royalties;McGraw Hill:Patents & Royalties;GRAIL:Consultancy, Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Henry Stewart Talks:Patents & Royalties;Iterion Therapeutics (formerly Beta Cat Pharmaceuticals):Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Leukemia & Lymphoma Society:Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal